Artificial Intelligence Explained – this comprehensive guide demystifies how AI transforms our daily lives, businesses, and industries. Whether you’re browsing personalized recommendations on streaming platforms, using voice assistants, or witnessing breakthroughs in healthcare diagnostics, artificial intelligence is everywhere. For beginners eager to understand this revolutionary technology, learning AI might seem overwhelming—but it doesn’t have to be. This guide will walk you through AI fundamentals, practical learning steps, free resources, and the tools you need to master artificial intelligence in 2025. From understanding what AI truly means to exploring how to learn AI step by step, this article serves as your complete roadmap to becoming AI-literate in today’s tech-driven world.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by computer systems, enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human cognition such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. Unlike traditional software that follows explicit programmed instructions, AI systems can analyze data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. The core difference lies in adaptability—while conventional programs execute predefined rules, AI learns from experience and improves performance over time through machine learning algorithms.
Simple Definition for Beginners
Think of AI as teaching computers to “think” and make decisions like humans do, but at much faster speeds and with the ability to process vast amounts of information. When you ask ChatGPT a question or use Google Gemini for research, you’re interacting with AI that has learned from billions of text examples. For those wondering how to learn artificial intelligence for beginners, it’s essential to grasp that AI isn’t magic—it’s mathematics, statistics, and computational algorithms working together.
Real-World Examples of AI
AI applications surround us daily: Netflix recommends shows based on viewing history, Spotify creates personalized playlists, autonomous vehicles navigate roads using computer vision, and Grammarly corrects writing using natural language processing. Healthcare providers use AI to detect diseases from medical imaging with greater accuracy than traditional methods, while financial institutions employ AI for fraud detection and algorithmic trading. Understanding these practical applications is the first step in learning AI online and recognizing its transformative potential.
AI vs Traditional Software
Traditional software operates on explicit if-then logic: if condition X occurs, execute action Y. AI systems, however, use probabilistic models and learn from data to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. This fundamental difference makes AI adaptable to new situations and capable of handling complex, unstructured data like images, speech, and text. For beginners exploring AI tools for free, understanding this distinction helps clarify why AI-powered applications like Canva (which uses AI for design suggestions) feel more intuitive than traditional design software.
History & Evolution of AI
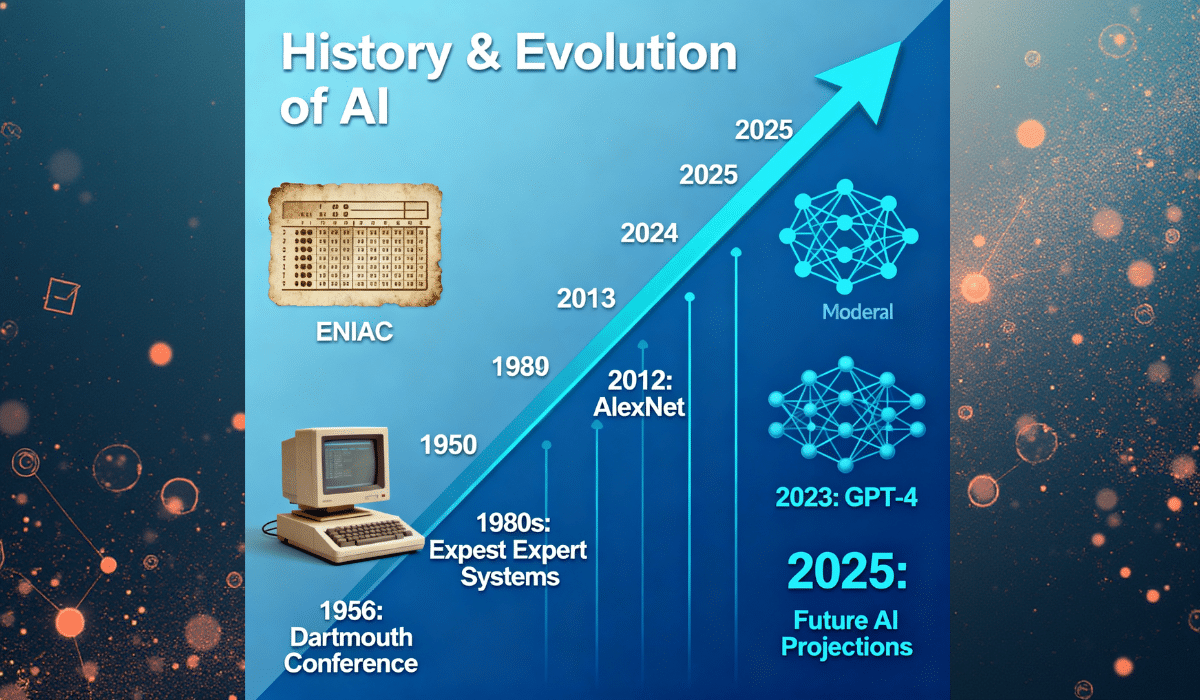
The journey of artificial intelligence began in 1950 when British mathematician Alan Turing proposed the famous “Turing Test” to determine whether machines could exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from humans. The term “artificial intelligence” was officially coined in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where pioneering researchers like John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Allen Newell gathered to explore machine intelligence. Early AI focused on symbolic AI—using logic and rules to solve problems—leading to expert systems in the 1970s and 1980s that could perform specialized tasks like medical diagnosis.
The AI Winters
The AI field experienced two major “winters”—periods of reduced funding and interest—first in the 1970s and again in the late 1980s to early 1990s. These occurred when early AI promises failed to materialize due to limited computational power, insufficient data, and overly ambitious expectations. Researchers found that symbolic AI couldn’t handle the complexity and ambiguity of real-world problems, leading to widespread skepticism about AI’s potential. However, these setbacks ultimately pushed the field toward more practical, data-driven approaches that would later revolutionize AI.
Modern AI Renaissance
The AI renaissance began in the 2010s with breakthroughs in deep learning, fueled by three key factors: massive datasets from the internet, powerful GPUs for parallel processing, and improved neural network architectures. In 2012, a deep learning model called AlexNet dramatically outperformed traditional computer vision systems in image recognition, marking a turning point. This led to rapid advances including Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeating world chess champions, voice assistants becoming mainstream, and the emergence of generative AI models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) that can write, code, and create content. By 2025, AI has become democratized with tools like ChatGPT reaching 321.6 million monthly users and platforms offering free AI courses for beginners to learn these technologies.
Timeline Highlights
Key milestones include: 1956 (Dartmouth Conference), 1997 (IBM’s Deep Blue defeats chess champion), 2011 (IBM Watson wins Jeopardy), 2012 (Deep learning breakthrough), 2016 (AlphaGo defeats Go champion), 2018 (GPT-1 released), 2022 (ChatGPT launches), and 2025 (AI reasoning models and agentic AI emergence). For those following A Beginner’s Guide to AI podcast or learning AI step by step, understanding this evolution provides crucial context for where the technology is headed.
Types of AI
Artificial intelligence is categorized into three primary types based on capability and scope: Narrow AI (also called Weak AI), General AI (Artificial General Intelligence or AGI), and Superintelligence. Understanding these distinctions is fundamental for anyone learning how to use AI effectively and recognizing current technological limitations versus future possibilities.
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI refers to AI systems designed to perform specific tasks within a limited domain, representing all AI applications currently in existence. Examples include ChatGPT for text generation, DeepL for translation (167 million monthly visits), Grammarly for writing assistance, and Remove.bg for image background removal. These systems excel at their designated functions but cannot transfer knowledge to unrelated domains—a chess-playing AI cannot suddenly diagnose diseases. Narrow AI powers AI tools like Canva (285.7 million monthly users), QuillBot, and Midjourney, making them accessible for beginners exploring how to learn AI tools for free. Despite being “narrow,” these systems have revolutionized industries and represent the practical AI you can self-study and apply immediately.
General AI (AGI)
Artificial General Intelligence represents hypothetical AI systems with human-like cognitive abilities—capable of understanding, learning, and applying knowledge across diverse domains just as humans do. AGI would possess common sense reasoning, emotional intelligence, creativity, and the ability to transfer learning from one context to another. As of October 2025, AGI remains theoretical despite significant research investments from organizations like OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic. Recent developments in AI reasoning models and Claude Opus 4 showcase progress toward more generalized capabilities, but true AGI is likely decades away. For beginners learning AI online, understanding that current free AI courses teach Narrow AI applications—not AGI—helps set realistic expectations.
Superintelligence
Superintelligence refers to AI that surpasses human intelligence across all domains—from scientific creativity to social skills and general wisdom. This purely speculative concept raises profound questions about AI safety, control, and ethical implications that researchers actively study. Prominent AI experts debate whether superintelligence would emerge gradually or suddenly (“intelligence explosion”), and what safeguards humanity needs before reaching that point. While exploring best AI courses for beginners, learners should focus on understanding current AI capabilities rather than speculative superintelligence scenarios. Organizations like Anthropic (creators of Claude) prioritize AI safety research specifically to address potential risks as systems become more capable.
Visual Comparison
| Type | Capability | Current Status | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow AI | Specialized single-domain tasks | Exists today | ChatGPT, Grammarly, Self-driving cars |
| General AI | Human-level intelligence across all domains | Theoretical research | None yet |
| Superintelligence | Exceeds human intelligence in all areas | Speculative future | None |
Following a roadmap to learn AI means starting with Narrow AI applications, understanding their architecture through online courses, and gradually building expertise.
AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning

The terms artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts with a hierarchical relationship. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone learning AI step by step and selecting appropriate AI tools or courses.
Artificial Intelligence (Broad Umbrella)
AI is the overarching field encompassing all techniques that enable machines to mimic human intelligence, including rule-based systems, expert systems, machine learning, and deep learning. It represents the broadest concept, dating back to the 1950s, and includes both learning-based and non-learning approaches. When you use AI tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity AI, or Microsoft Copilot, you’re interacting with AI systems built on machine learning foundations. For beginners exploring how to self-study artificial intelligence free, understanding AI as the parent category helps organize learning paths.
Machine Learning (Subset of AI)
Machine learning is a subset of AI focused on algorithms that learn patterns from data without explicit programming for every scenario. ML systems improve performance through experience—training on datasets to recognize patterns, make predictions, or classify information. Common ML techniques include supervised learning (learning from labeled data), unsupervised learning (finding patterns in unlabeled data), and reinforcement learning (learning through trial and error). Tools like Google AI Studio (80% popularity growth in 6 months) and platforms offering AI for beginners free courses teach ML fundamentals as the foundation for modern AI. If you’re learning how to learn AI tools for free, understanding ML algorithms helps you grasp why tools like DeepSeek (88.6% growth) or Claude function the way they do.
Deep Learning (Subset of Machine Learning)
Deep learning is a specialized subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers (hence “deep”) to process information hierarchically. Inspired by the human brain’s structure, deep learning excels at handling unstructured data like images, audio, and text—powering applications from facial recognition to generative AI tools. Modern breakthroughs including GPT models, Gemini Advanced, image generators like Midjourney and Stable Diffusion, and voice cloning tools like ElevenLabs all rely on deep learning architectures. For those learning AI online through free courses, deep learning represents the cutting edge but requires understanding ML fundamentals first.
Analogy for Clarity
Think of AI as transportation (the broadest category), machine learning as vehicles (a specific type of transportation), and deep learning as sports cars (a high-performance type of vehicle). This hierarchical relationship means all deep learning is machine learning, all machine learning is AI, but not all AI is machine learning. When exploring AI tools or following a roadmap to learn AI, starting with foundational ML concepts before advancing to deep learning creates a logical progression.
Key AI Technologies
Modern artificial intelligence encompasses several specialized technologies, each addressing specific challenges in mimicking human intelligence. Understanding these core technologies is essential for anyone learning how to use AI effectively and exploring practical applications through AI tools.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in meaningful ways. NLP powers ChatGPT (321.6 million monthly users), translation tools like DeepL (167 million monthly visits), writing assistants like Grammarly and QuillBot (100.9 million visits), and conversational AI like Claude and Gemini. Advanced NLP applications include sentiment analysis, text summarization, question-answering systems, and chatbots that understand context and nuance. For beginners exploring free AI courses, NLP represents one of the most accessible entry points with immediate practical applications. Tools like Perplexity AI (10.6 million monthly visits) demonstrate how NLP combines with real-time web search to create powerful research assistants. Anyone learning AI step by step should experiment with NLP tools and explore courses covering transformer architectures that revolutionized language understanding.
Computer Vision
Computer vision enables machines to interpret and understand visual information from images and videos, mimicking human sight. Applications range from facial recognition and medical image analysis to autonomous vehicle navigation and augmented reality. Popular tools include Remove.bg (41.7 million monthly visits) for background removal, Midjourney and Leonardo.ai for AI image generation, and CapCut for video editing. Computer vision relies heavily on deep learning architectures called convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that process visual data hierarchically. For those learning AI online or exploring how to self-study artificial intelligence free, computer vision projects offer engaging hands-on learning opportunities.
Robotics and Reinforcement Learning

AI robotics combines hardware with intelligent software, enabling machines to perform physical tasks autonomously—from manufacturing robots to delivery drones. Reinforcement learning, the AI technique behind many robotic systems, teaches agents to make decisions through trial-and-error interactions with environments, maximizing cumulative rewards. This technology powered DeepMind’s AlphaGo victory and now drives autonomous vehicles, robotic surgery assistants, and warehouse automation. Recent 2025 trends show AI agents becoming more autonomous, with Microsoft Copilot and other systems performing multi-step tasks independently. Beginners interested in robotics can start with simulation environments before moving to physical systems, following roadmaps to learn AI that include reinforcement learning fundamentals.
AI Analytics and Decision Systems
AI analytics applies machine learning to vast datasets, uncovering patterns, predicting outcomes, and supporting data-driven decision-making. Business intelligence platforms, predictive maintenance systems, financial forecasting tools, and customer behavior analytics all rely on AI to process information beyond human analytical capacity. Tools like Zapier (4.4 million monthly visits) integrate AI automation across applications, while enterprise platforms from Microsoft, Google, and Amazon AWS offer AI analytics capabilities. For professionals learning AI tools for free, understanding analytics applications opens career opportunities across industries.
Generative AI
Generative AI represents the newest frontier, creating original content—text, images, audio, video, and code—rather than merely analyzing existing data. This technology powers ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, image generators like Midjourney and Stable Diffusion, video tools like Runway and Luma AI, and audio platforms like ElevenLabs and Suno. The 2025 AI landscape shows explosive growth in generative tools, with DeepSeek (88.6% growth) and NotebookLM (57% growth) leading adoption. For beginners exploring AI prompts and practical applications, generative AI offers immediate value through content creation assistance.
Popular AI Applications Today
Artificial intelligence has transitioned from experimental technology to essential infrastructure across industries, transforming how businesses operate and consumers interact with services. Understanding real-world AI applications helps beginners recognize opportunities for learning AI tools and applying them practically.
AI in Business and Enterprise
Businesses leverage AI for automation, customer service, data analytics, and decision-making—with research showing AI adoption accelerating in 2025. Customer service chatbots like Character.ai (20.3 million monthly visits) and Microsoft Copilot (13.4 million visits) handle inquiries, while AI analytics platforms predict market trends and optimize supply chains. Marketing departments use AI tools like Copy.ai, Jasper, and Writesonic for content creation, while Canva (285.7 million monthly users) employs AI for design automation. Enterprise automation platforms like Zapier and n8n integrate AI across workflows, reducing manual tasks. Enterprise customers demand AI solutions focused on optimized performance, profitability, and security. For professionals exploring how to learn AI online, understanding business applications clarifies career relevance.
Healthcare and Medical AI
Healthcare represents one of AI’s most impactful application areas, with systems diagnosing diseases from medical imaging, predicting patient outcomes, accelerating drug discovery, and personalizing treatment plans. AI tools for genomics and cancer research demonstrate how AI processes complex biological data beyond human analytical capacity. AI-powered diagnostic tools detect diabetic retinopathy, skin cancer, and pneumonia from images with accuracy matching or exceeding specialist physicians. Robotic surgery systems use computer vision and AI decision-making for precision procedures, while natural language processing extracts insights from medical records. For students learning AI step by step, healthcare applications showcase AI’s societal impact beyond commercial uses.
Finance and Algorithmic Trading
Financial institutions employ AI for fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading, risk assessment, and personalized banking experiences. AI systems analyze transaction patterns in real-time to flag suspicious activities, while machine learning models predict loan defaults more accurately than traditional credit scoring. Algorithmic trading platforms use AI to process market data, news sentiment, and complex patterns at speeds impossible for human traders. Robo-advisors powered by AI provide investment recommendations tailored to individual risk profiles and financial goals. Financial firms are investing heavily in AI infrastructure for competitive advantage. Beginners interested in AI for trading or finance can explore specialized courses and tools, though this represents a more advanced application requiring domain knowledge.
Education and Personalized Learning
Educational technology increasingly incorporates AI for personalized learning paths, intelligent tutoring systems, automated grading, and content generation. Platforms use AI to adapt difficulty levels based on student performance, identify knowledge gaps, and recommend targeted resources. NotebookLM (473,600 monthly visits, 57% growth) exemplifies AI-powered research and note-taking tools for students. Language learning applications employ AI speech recognition and personalized feedback, while AI writing assistants like Grammarly, QuillBot, and Wordtune help students improve composition skills. The accessibility of free AI courses for beginners demonstrates AI’s role in democratizing education itself. For those self-studying artificial intelligence free, educational AI tools provide both learning resources and practical examples.
Content Creation and Creative Industries
The generative AI revolution has transformed creative workflows, with tools generating text, images, videos, music, and code. Content creators use ChatGPT for writing, Midjourney and Leonardo.ai for visuals, Runway and HeyGen for videos, and Suno for music. Design platforms like Canva integrate AI features for non-designers, while video editing tools like CapCut, Descript, and Opus Clip automate complex editing tasks. Marketing professionals leverage AI tools for social media content, ad copy, and campaign optimization. The 2025 AI trends show content creation as the fastest-growing consumer AI application, with tools like Perplexity AI expanding from search into comprehensive productivity suites. Exploring creative AI applications offers beginners immediate, tangible results while learning how to use AI practically.
Benefits & Limitations of AI
Understanding both the advantages and constraints of artificial intelligence provides a balanced perspective essential for anyone learning AI step by step or implementing AI tools professionally.
Key Benefits of AI
Automation and efficiency stand as AI’s primary advantages—machines handle repetitive tasks faster and more consistently than humans, freeing workers for creative and strategic activities. AI systems operate 24/7 without fatigue, process vast datasets instantly, and scale effortlessly as demands increase. Enhanced decision-making emerges from AI’s ability to analyze complex patterns humans might miss, supporting data-driven choices across industries from healthcare diagnostics to financial forecasting. Personalization at scale allows businesses to tailor experiences for millions of users simultaneously—evident in recommendation engines, targeted marketing, and adaptive learning platforms. Cost reduction follows from automation, with enterprises achieving significant operational savings through AI adoption. AI is becoming “more efficient, affordable, and accessible,” with open-weight models closing performance gaps with proprietary systems. For beginners exploring how to learn AI tools for free, these benefits translate to accessible, powerful technologies democratizing capabilities once limited to large organizations.
Current Limitations
Data dependency represents AI’s fundamental constraint—systems require massive, high-quality datasets for training, and performance degrades with poor or biased data. Lack of common sense and contextual understanding plague even advanced AI; systems excel at patterns but struggle with reasoning outside training distributions. Interpretability challenges (the “black box problem”) make it difficult to understand why AI systems make specific decisions, raising concerns in critical applications like medical diagnosis or legal judgments. Computational costs for training large models demand enormous energy and processing power, creating environmental and accessibility barriers. Security vulnerabilities include adversarial attacks that fool AI systems and potential misuse for creating deepfakes, misinformation, or autonomous weapons. For those learning AI online through free courses, understanding limitations helps set realistic expectations and identify areas for responsible development.
AI Myths vs Facts
Artificial Intelligence is surrounded by both hype and misunderstanding. Knowing the facts helps users set realistic expectations and avoid common pitfalls.
Common Myths and Realities
- Myth: AI always makes perfect, unbiased decisions.
- Fact: AI systems can inherit bias from data and require regular testing and oversight.
- Myth: AI understands emotions and context like humans.
- Fact: Most AI only analyzes patterns in data; human-like reasoning and empathy are still limited.
- Myth: AI will replace most jobs soon.
- Fact: AI automates repetitive tasks, but many roles adapt and new opportunities emerge in collaboration with AI.
- Myth: AI is unsafe and uncontrollable.
- Fact: AI depends on strict programming, ongoing audits, and ethical governance to ensure safe use.
- Myth: Only tech experts can work with AI.
- Fact: Many no-code and user-friendly AI tools empower non-specialists to leverage AI in everyday tasks.
Understanding AI myths vs facts leads to informed decisions, responsible technology use, and realistic expectations for the future.
Ethical and Practical Considerations
Bias and fairness issues arise when AI systems inherit prejudices from training data, potentially amplifying discrimination in hiring, lending, or criminal justice. Privacy concerns intensify as AI requires extensive personal data, raising questions about consent, surveillance, and data protection. Job displacement fears accompany automation, though experts debate whether AI creates more jobs than it eliminates. Accountability questions emerge when AI makes harmful decisions—determining responsibility between developers, deployers, and users remains complex. Organizations like Anthropic (creators of Claude) prioritize “helpful, honest, and harmless” AI development. The 2025 AI trends emphasize building AI systems that meet enterprise needs for security, profitability, and optimized performance. For beginners self-studying artificial intelligence free, engaging with ethics courses and resources develops crucial responsible AI practices.
Comparison Table
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| 24/7 availability and consistency | Requires massive training data |
| Processes vast datasets instantly | Lacks common sense reasoning |
| Enhances decision-making accuracy | “Black box” interpretability issues |
| Enables personalization at scale | High computational and energy costs |
| Reduces operational costs | Vulnerable to adversarial attacks |
| Automates repetitive tasks | Can perpetuate bias and discrimination |
| Accessible through free tools | Privacy and surveillance concerns |
Understanding this balance helps learners approach AI tools and applications with appropriate expectations and ethical awareness.
Future of AI: Trends & Predictions
The artificial intelligence landscape in 2025 shows explosive growth with clear trajectories toward more capable, autonomous, and integrated systems. Understanding emerging trends helps beginners learning AI step by step focus efforts on relevant skills and technologies.
Generative AI Expansion
Generative AI dominates the 2025 landscape, with tools like ChatGPT (321.6 million monthly users), Claude Opus 4, and Gemini leading adoption. Reports identify generative AI as “the next productivity frontier,” transforming content creation, software development, and knowledge work. Fast-growing tools include DeepSeek (88.6% six-month growth), Google AI Studio (80% growth), and NotebookLM (57% growth)—all offering free access that democratizes capabilities. AI reasoning emerges as a key focus, with models developing more sophisticated problem-solving abilities beyond pattern matching. For those exploring how to learn AI tools for free, the generative AI wave provides accessible entry points through platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude.
Agentic AI and Autonomous Systems
AI agents—systems that perform multi-step tasks autonomously with minimal human supervision—represent a major 2025 trend. Unlike current AI that responds to prompts, agentic systems plan, execute, and adapt strategies to achieve goals. AI is evolving “from a tool for work and home to an integral part of both,” with Copilot and similar systems handling increasingly complex workflows. Autonomous vehicles, robotic process automation, and AI-powered scientific research tools demonstrate this shift toward greater autonomy. For beginners learning AI online, understanding agent architectures and reinforcement learning becomes increasingly relevant.
Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, 2025 AI trends emphasize collaboration models where AI augments human capabilities. Analysis describes AI adoption giving way to “AI-human partnerships” that combine machine efficiency with human creativity, empathy, and judgment. Tools like Perplexity AI (10.6 million monthly visits) exemplify this by combining AI processing with human-guided research. Systems are being designed for “near infinite memory,” enabling AI assistants to maintain context across extended interactions. For professionals exploring best AI courses for beginners, developing skills in prompt engineering and AI tool integration supports effective collaboration.
AI in Cybersecurity and Policy
Cybersecurity emerges as both an AI application area and concern, with systems detecting threats while adversaries use AI for sophisticated attacks. AI-powered threat detection and response systems are becoming standard across enterprises. Simultaneously, policy discussions intensify around AI regulation, with governments worldwide developing frameworks for responsible deployment. Trade policies create uncertainties for AI companies navigating international markets. For learners following a roadmap to learn AI, understanding regulatory and security contexts prepares for professional responsibilities.
Democratization and Accessibility
The 2025 AI landscape shows continued democratization through free tools, courses, and open-source models. Open-weight models are closing the gap with closed models, reducing barriers to entry. Platforms offering free AI courses for beginners enable anyone to self-study artificial intelligence free. Popular free tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, DeepSeek, and Google AI Studio provide professional-grade capabilities without cost barriers. This accessibility trend means beginners can immediately start learning how to use AI through hands-on experimentation with AI tools and AI prompts.
How to Learn AI as a Beginner
Mastering artificial intelligence requires a structured approach combining theoretical understanding with practical application. This comprehensive roadmap addresses how to learn AI step by step, from foundational concepts to hands-on projects.
Step 1: Build Mathematical Foundations
Start with essential mathematics—linear algebra (vectors, matrices), calculus (derivatives, gradients), probability (distributions, Bayes’ theorem), and statistics (hypothesis testing, regression). These fundamentals underpin machine learning algorithms and help understand how AI systems learn from data. Free resources include Khan Academy for mathematics basics, MIT OpenCourseWare for advanced topics, and 3Blue1Brown YouTube channel for visual explanations. For those wondering how to self-study artificial intelligence free, dedicating 2-3 months to mathematical foundations prevents frustration later. Don’t aim for perfection—learn concepts as needed while building projects.
Step 2: Master Python Programming
Python dominates AI development due to libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, NumPy, and pandas. Begin with Python basics (variables, loops, functions) through Codecademy, Python.org tutorials, or university-level free courses. Progress to data manipulation with pandas and visualization with matplotlib. Practice coding daily through platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, or Kaggle. Seven-week free courses combine programming with AI concepts, exploring technologies behind game-playing engines, handwriting recognition, and machine translation. For beginners learning AI online, Python proficiency accelerates understanding of AI implementations.
Step 3: Take Structured AI Courses
Enroll in comprehensive free AI courses for beginners from reputable institutions. Top recommendations include multiple platforms offering courses covering generative AI from the ground up, including introductions to large language models. Courses cover AI basics through neural networks and deep learning. Comprehensive AI fundamentals with practical applications are available from various providers. Free online courses for non-experts cover what AI is, what’s possible, and societal impacts like Elements of AI. Specialized AI courses from platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity provide certificates upon completion. Follow a roadmap to learn AI by completing introductory courses before advancing to specialized topics.
Step 4: Hands-On Practice with AI Tools
Practical experimentation accelerates learning—immediately start using AI tools to understand capabilities and limitations. Experiment with:
- ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini for natural language processing and prompt engineering
- Google Colab for free cloud-based Python notebooks with GPU access
- Hugging Face (3 million monthly visits) for pre-trained models and datasets
- Kaggle for datasets, competitions, and community learning
The fastest-growing free AI tools like DeepSeek, Google AI Studio, and NotebookLM offer cutting-edge capabilities without cost barriers. Building projects—image classifiers, chatbots, recommendation systems—solidifies theoretical knowledge.
Step 5: Join Communities and Stay Updated
Engage with AI communities on Reddit (r/learnmachinelearning, r/artificial), Discord servers, Stack Overflow, and Twitter/X. Follow industry leaders, read research papers from arXiv, and listen to AI podcasts like “A Beginner’s Guide to AI podcast”. Annual AI reports provide comprehensive updates on industry trends. Online communities emphasize collaborative learning, with curated lists of multiple free AI courses covering beginner through advanced levels. For those learning how to use AI, staying current with 2025 AI trends ensures relevant skill development.
Step 6: Specialize and Build Portfolio
After mastering fundamentals, specialize in areas aligning with interests—computer vision, NLP, reinforcement learning, or generative AI. Build a portfolio showcasing projects on GitHub, write blog posts explaining concepts, or contribute to open-source AI projects. Participate in Kaggle competitions to solve real-world problems and learn from top practitioners. This practical experience demonstrates skills to employers more effectively than courses alone. For comprehensive best AI courses for beginners, combine theoretical learning with consistent project building.
Key AI Resources
Accessing quality AI learning resources is crucial for anyone learning artificial intelligence for beginners or advancing existing skills. This curated collection spans courses, research materials, tools, and communities supporting self-directed learning.
Free Online Courses
Multiple platforms offer comprehensive AI training programs:
- Coursera – AI courses from top universities
- edX – University-level AI programs
- Udacity – Nanodegree programs in AI
- Elements of AI – Beginner-friendly introduction
- Google AI – Free AI courses and resources
- Microsoft Learn – AI fundamentals training
- Fast.ai – Practical deep learning courses
Research Papers and Academic Resources
Stay current with cutting-edge AI research through arXiv.org, an open-access repository for computer science papers including the latest AI breakthroughs. Papers with Code connects research publications with code implementations, enabling hands-on learning from academic work. Google Scholar and Semantic Scholar provide searchable databases of AI literature. For beginners self-studying artificial intelligence free, reading simplified research summaries before tackling technical papers builds comprehension.
AI Tools and Platforms
Practical experience requires access to AI tools—fortunately, most leading platforms offer free tiers:
- ChatGPT – Conversational AI (321.6M users)
- Claude – Advanced AI assistant
- Gemini – Google’s AI platform
- Google Colab – Free Python notebooks with GPU
- Hugging Face – Pre-trained models and datasets
- Kaggle – Datasets, competitions, learning
- DeepSeek – Fast-growing AI tool (88.6% growth)
- Google AI Studio – AI development platform
- NotebookLM – AI research assistant
Explore comprehensive AI tools collections and learn effective AI prompts to maximize tool utility.
Communities and Forums
Join communities for peer support:
- Reddit – r/learnmachinelearning, r/artificial, r/MachineLearning
- Stack Overflow – Technical Q&A
- Discord – AI learning servers
- Twitter/X – Follow AI researchers and practitioners
- LinkedIn – Professional networking
Books and Documentation
Essential resources include:
- Official documentation for TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn
- Towards Data Science on Medium
- Machine Learning Mastery tutorials
- Analytics Vidhya resources
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence Explained – this guide has provided you with everything needed to understand and master AI fundamentals in 2025. Artificial intelligence represents one of the most transformative technologies of our era, reshaping industries, augmenting human capabilities, and creating unprecedented opportunities for those who understand its fundamentals. We’ve walked you through AI basics—from definitions and history to types, technologies, applications, and practical learning pathways. The democratization of AI through free courses, accessible AI tools, and open-source resources means anyone can start learning AI step by step today. Whether you’re exploring how to learn artificial intelligence for beginners, seeking best AI courses, or wondering how to use AI tools for free, the resources and roadmap provided offer clear starting points. As AI continues evolving with trends toward generative AI, autonomous agents, and human-AI collaboration, building foundational knowledge now positions you for success in an AI-driven future. Begin your AI journey by exploring AI tools and mastering effective AI prompts to unlock this technology’s transformative potential.
FAQ
Q1: What is AI and why is it important?
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems capable of performing tasks typically requiring human intelligence—learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. AI matters because it transforms industries by automating processes, enhancing decision-making through data analysis, personalizing experiences at scale, and solving complex problems beyond human analytical capacity. The 2025 AI landscape shows AI becoming “more efficient, affordable, and accessible,” democratizing capabilities once limited to large organizations and creating new economic opportunities. From healthcare diagnostics to financial forecasting, creative content generation to scientific research, AI amplifies human capabilities across domains.
Q2: How can beginners learn AI step by step?
Learning AI step by step follows a structured path.
(1) Build mathematical foundations in linear algebra, calculus, probability, and statistics.
(2) Master Python programming including data manipulation libraries.
(3) Complete free AI courses covering fundamentals.
(4) Practice hands-on with AI tools like ChatGPT, Google Colab, and Kaggle.
(5) Join communities on Reddit, Discord, and Stack Overflow for peer support.
(6) Build projects showcasing skills and specialize in areas matching interests.
This roadmap to learn AI typically takes 6-12 months for foundational competency, with continuous learning thereafter as the field evolves.
Q3: Are there free AI courses for beginners?
Yes, numerous institutions offer free AI courses for beginners with completion certificates. Platforms like Coursera, edX, Udacity, and Elements of AI provide comprehensive programs covering generative AI from introduction through advanced topics. Google AI and Microsoft Learn offer practical, hands-on training. Fast.ai provides practical deep learning courses. Online communities curate extensive lists of free AI courses covering beginner through advanced levels.
Q4: How to learn to use AI tools for free?
Learning AI tools for free starts with hands-on experimentation with popular platforms. ChatGPT (321.6 million monthly users), Claude, and Gemini offer free tiers for natural language processing practice. Fast-growing free tools include DeepSeek (88.6% growth), Google AI Studio (80% growth), and NotebookLM (57% growth). Google Colab provides free cloud-based Python notebooks with GPU access for training models. Hugging Face offers pre-trained models and datasets for experimentation. Kaggle combines learning resources with practical competitions. Explore AI tools collections and master AI prompts to maximize effectiveness.
Q5: How can I self-study AI online?
Self-studying artificial intelligence free requires structured planning and discipline. Create a learning schedule dedicating consistent time daily (even 30-60 minutes). Follow established curricula from free online courses rather than random tutorials to ensure comprehensive coverage. Balance theory with practice—implement concepts immediately through projects on Google Colab or Kaggle. Join communities like Reddit’s r/learnmachinelearning for accountability, resource recommendations, and troubleshooting. Document learning through blog posts or GitHub repositories, reinforcing understanding while building portfolios. Set milestones (completing courses, building specific projects) to track progress. Successful self-study combines best AI courses for beginners with consistent hands-on practice and community engagement.
Q6: What are the best AI resources for beginners?
Best AI resources for beginners span multiple formats. For courses: Coursera, edX, Udacity, Elements of AI, Google AI, and Microsoft Learn. For practice: Google Colab, Kaggle, Hugging Face, ChatGPT, and emerging tools like DeepSeek and Google AI Studio. For research: arXiv and Papers with Code. For community: Reddit (r/learnmachinelearning), Stack Overflow, Discord servers, and Twitter/X AI communities. For documentation: official TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn guides. Combining these resources creates comprehensive pathways for learning AI online.